Back pain, according to statistics, about 80% of people in different age groups experience this unpleasant and frightening symptom at least once in their lifetime. At the same time, it is important to be able to differentiate between situations where painful feelings can interfere and when you don’t have to worry.
Of course, if the onset of pain was preceded by physical exertion or a minor blow that dissipated within 2-3 days, there is no cause for concern. But if your back hurts badly for a long time and the pains don’t look like muscle aches, rush to the doctor.
Why does my back hurt
The causes of back pain vary from minor external factors to the development of all sorts of pathological processes, many of which are also present.
However, doctors still identify the 3 most common causes:
- Non-specific pains
- . . . This point can also include the painful feelings that occur after hypothermia, in which case they say - "chilled back. "
- Radiating pains- slightly rarer but cannot be ruled out. This includes diseases of the internal organs that are found in other parts of the body. For example, the development of tumors and pulmonary tuberculosis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the heart and others. In each of these cases, the pain may radiate (give) to the back in different parts of it.
- Mechanical injuries and pathologies of the spine- pain in the spine is also caused by a number of factors, we talk about pathological processes. These include any disease of the spine, starting with injuries (bruises, fractures, and so on) and ending with osteochondrosis, radiculitis, hernia formation, and other pathologies affecting the spine of the spinal region.
These are usually the main causes of back pain. All of these problems threaten severe spinal dysfunction and require mandatory medical attention.
In some cases, without proper treatment, there is a risk of developing serious problems that threaten serious complications. If the tissues in the spine or spinal cord are affected, there is a risk of paralysis of the limbs or even the whole body.
Symptoms
In order to see a doctor in time and describe his or her complaints correctly, you need to imagine the symptoms.
However, the symptoms of back pain can vary slightly, and given the fact that the pain itself is a symptom, its main manifestations, which differ in nature and location, should be highlighted:
- Feelings of pain by nature: sharp, dull, stinging, cutting, sore, pulling, burning, etc.
- Painful feelings are strong, moderate, and weak, these indicators are unique to each person. However, these should be considered, for example, when determining the treatment of chronic back pain.
- Complete back pain is quite rare. More often, painful feelings are either point-like or assigned to a separate part of the spine (neck, chest, lumbar).
- However, there is also occasional pain in the upper spine (or any other). In this case, the pain syndrome affects other parts of the back, often referred to as migration.
- As a general rule, acute spinal pain is the most unpleasant and affects daily life, but is often wavy and easier to treat. At the same time, dull pains are less intense but are constantly present, fixate for a longer period of time, and respond less well to therapy.
These are general guidelines for painful feelings in different areas of the back. But in addition to understanding the general symptoms of pain, it is also important to know that the clinical picture may change depending on the disease. So in one case there is pain between the vertebrae of the cervical spine, in another case it is localized in the lumbar region and of a different nature.
Therefore, it is worth examining the symptoms of various pathological processes associated with back pain separately.
Osteochondrosis
If you have back pain in your back, the most likely diagnosis will be osteochondrosis, as this disease is more common than others. It is also important to understand that doctors distinguish three types of osteochondrosis: neck, chest, and lumbar.
In both cases, intervertebral pain is associated with different parts of the spine. The disease itself involves the destruction of cartilage tissue in the intervertebral discs, while the pathological process also occurs in the vertebrae because they are erased due to a narrowing of the gap between them.
The main symptom of the disease is pain, but clinical signs of the nervous system may also be present, as the spinal cord is most likely affected and its roots are damaged.
Myositis
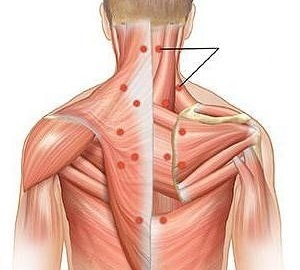
A rare disease characterized by an inflammatory process in the muscle tissues of the body, including the back. More often, myositis is accompanied by painful pain, but sharp pain or so-called back pain is also possible.
Pain syndrome is localized directly at the site of inflammation of muscle tissue, but pain can radiate to nearby areas.
Spondylosis
If the spine hurts, spondylosis may be one of the likely causes. This pathology is characterized by growth of vertebral bone tissue as well as dystrophic changes. In this case, during physical exertion, painful feelings occur due to a long stay in one of the positions, such as sitting.
Sciatica
The term refers to constriction and further inflammation of the sciatic nerve. The pathological process is accompanied by cuts, punctures and sharp pains. In sciatica, the pain is not felt all the time, it occurs suddenly, it rolls in waves.
Severe sciatica, directly at the site of injury or inflammation. However, due to the fact that the sciatic nerve is very long, there are painful feelings in different areas, most often pain in the legs.
Osteoporosis
The disease is caused by a lack of calcium in the body. As a result, bone tissues along the entire spinal column lose their elasticity and stiffness, causing microtrauma and cracks everywhere.
In this pathological process, the whole spine hurts, especially in the later stages of the disease.
Herniated disc
Acute and severe spinal pain may be evidence of disc herniation. However, pain syndrome is constant but is exacerbated by physical exertion, bending, coughing, sudden or careless movements.
In most cases, a hernia forms in the lumbar spine, which is explained by the vulnerability of this area to excessive loads and weight lifting. The hernia often presents as a complication of osteochondrosis due to the peculiarities of the process of this pathology.
In this case, the hernia is not only dangerous with pain, there is a risk of pinching the nerve branches of the spinal cord and the development of neurological symptoms.
Excessive spinal movement
This problem is also called spinal hypermobility or spinal instability. A clear sign of pathology is painful feelings that increase with intense physical exertion and weight lifting. The back painful feelings are volatile in nature or subside and then suddenly reappear.
The cervical spine is most severely affected, if the disease progresses, one has a hard time holding one's head.
Scoliosis
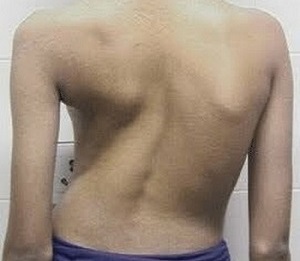
Oddly enough, curvature of the spine is a direct cause of pain. One of the most common problems is scoliosis. The pain of scoliosis is more muscular in nature. This is due to increased strain on the back muscles while others relax.
In scoliosis, due to the curvature of the spine, each vertebral disc compresses and the cartilage tissue deforms.
The painful feelings associated with scoliosis are constant, painful, or pulling, of low intensity, and in rare cases, the pain is strong and sharp.
Spinal cord injury
Of course, any mechanical damage, even minor, is painful. In this case, the more severe the pain, the more severe the damage, and sometimes even seemingly insignificant injury can cause acute pain, which can indicate severe internal injuries. In this case, blows, bruises, sprains, displacements are considered, but fractures are the most severe types of injuries.
It’s remarkable that old, long-healing injuries feel felt decades later. So back and neck pain can remind you how you fell on the ice as a child.
Bechterew's disease
This dangerous disease is also called ankylopathic spondyloarthritis. Pathology is characterized by a chronic inflammatory process in the joints, in other words, inflammation of the spine.
The ankylopathy of spondylitis is associated with severe pain, and the intensity of the pain syndrome is high from the onset of the pathological process and will only increase in the future. In this case, the pain increases after rest and depending on the change of weather, but they are well controlled by the drugs of the NSAID group and physiotherapy.
Oncological diseases
Cancer is the most dangerous pathology with a clear sign of pain. In this case, pain syndrome occurs in both benign and malignant tumors when they are localized and pressurized not far from the spinal column.
Metastases are an even more dangerous manifestation of oncology. In this case, the pains are constant and strong, haunting a person always and everywhere, regardless of the position of the body or any action. It hurts just as hard when lying back.
Kidney disease
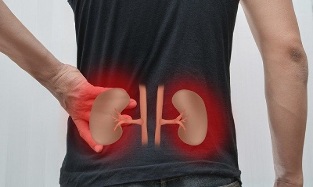
The causes of lower back pain are not always related to back problems. Due to the anatomical location of the kidneys, the pathologies that affect them also respond to severe pain in the lumbar spine.
Pain can be dull, pulling, or sharp stinging, the intensity of which varies depending on the disease and the degree of progression.
Here, it is important to understand that painful feelings can be on either side or only one side, indicating which kidney is involved in the pathological process.
Cardiovascular pathology
It is a misconception that in cardiovascular disease, pain occurs only in the chest region. For example, in ischemic heart disease and myocardial infarction, painful feelings surround, radiating to the back of the chest region. They are sharp, stinging in nature and occur suddenly.
Cardiovascular pathologies include aneurysms of the aortic sections, in which there is sharp pain in the chest region near the spine.
Gastrointestinal pathology
Gastrointestinal diseases often also provoke back pain, but in such cases there are always a number of distinctive clinical symptoms. In addition to pain, indigestion, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or diarrhea and general malaise are also present.
Infections
Bone tuberculosis is the most serious and dangerous of the infectious diseases associated with back pain. The disease involves severe pathological processes in the tissues of the bones, the entire spine hurts. Pain is different in nature, sometimes pulling, sometimes stabbing, but always constant.
Respiratory Diseases
The lungs occupy most of the body's chest, so lung disease is often accompanied by back pain. Such diseases include pneumonia, tuberculosis, pleurisy and so on.
With such conditions, the pain is increased during coughing, sneezing, deep breathing, yawning. In addition, the clinical picture is enriched by coughs, shortness of breath and other similar symptoms.
Congenital diseases
The factor of congenital anomalies is extremely rare, but it does occur. In this case, the main suspicion is a congenital excess or insufficient number of vertebrae in the spine. This affects the muscles and ligaments, the structure of the body, threatens the protrusion of the spine or compression, which is invariably accompanied by pain.
Pregnancy and childbirth
Pregnancy is also a cause of painful back symptoms.
Spine pain and other similar problems are more common in the third trimester, depending entirely on the growth of the fetus and the increased load on the spine.
In such cases, the pain usually becomes dull, tense, subsides, or temporarily disappears after a short rest when the expectant mother goes to bed.
Inflammatory processes
A wide variety of inflammatory processes lead to the development of pain syndrome, some of which we have already discussed. Take spondyloarthritis (ankylosing spondylitis). This pathology begins in the lumbosacral region, followed by inflammation and concomitant painful back pain on the spine.
Pain radiating to the spine
As mentioned at the outset, there is a class of pain called radiation. This means that back pain "releases" the spine from other parts or organs in which the disease has flared up. Let’s talk in more detail about such pains.
Pathologies of the heart and large blood vessels
The most likely diseases of the cardiovascular system, accompanied by back pain, have been mentioned earlier. It is only to be understood that in addition to pain, such pathologies are accompanied by violations of blood pressure, arrhythmia, and pallor of the skin, which is their distinguishing feature.
Diseases of the gallbladder
The clearest example of such an abnormal process is cholecystitis, which leads to the irradiation of pain in the right shoulder blade and the middle part of the spine in the chest region.
The acute form of the disease is accompanied by strong cuts, while the chronic one is more difficult to diagnose because the pain is inconsistent and low in intensity.
Pancreatic lesions
The most common disease of the pancreas is inflammation of the pancreas. The clinical sign of such a condition is abdominal pain, but they are also surrounded by a sharp, stabbing character. However, in addition to the pain, the patient suffers from nausea and vomiting, and painful feelings occur after eating fatty, sweet, fried foods.
Pathology of the kidneys and upper urinary tract
Kidney and urinary tract diseases are also painful and usually intense. Severe pain occurs during urolithiasis, but is not only felt in the lumbar region. There is severe discomfort in the lower abdomen and groin.
Diagnostics
As the huge list of possible problems and possible diseases shows, in order to eliminate back and spine pain, the main cause of its occurrence must be determined.
To do this, be sure to see a doctor and perform a full differential diagnosis that includes the following:
- Radiographyis a simple but fairly effective method for determining the condition of the spine, allowing the detection of deformities and various pathologies.
- CT- Computed tomography more accurately reveals the pathology of intervertebral discs and vertebrae.
- MRI- magnetic resonance imaging is an even more advanced and effective diagnostic method that not only presents probable problems with the structure of vertebrae and intervertebral discs, but also allows the identification or exclusion of nerve involvement in a pathological process.
If the above surveys have failed, please contact narrow profile professionals in other areas. Perhaps the problem is in the disease of the heart, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, pelvic organs and so on.
How to treat back pain
Treating acute back pain requires a comprehensive and systematic approach. The methods of combat become clear after a full examination and accurate diagnosis. It is also important to understand that in case of such problems, be sure to consult a specialist, self-healing is not unacceptable at all.
Your doctor will determine your treatment regimen, which will likely include medication, physiotherapy, exercise, and massages.
Physiotherapy
This is one of the main methods for treating spinal pathologies.
Treating back pain involves the following procedures:
- Electrophoresis.
- Exposure to ultrasound.
- Laser therapy;
- Magnetotherapy.
Treatment is performed in 7-10 or longer procedures, with an interval of 3-5 days between procedures.
Tournament
Physiotherapy and gymnastics are also included in the treatment of pain syndrome, however, these techniques are mainly used for healing when there is no more severe pain. Exercise is necessary to restore the flexibility and mobility of the muscle, to keep it in good condition and to accelerate the back injuries.
It is important to continue the first sessions with a physiotherapist who will set the methodology and distribute the workload, teaching you how to do it right. In the future, classes will be conducted at home and, most importantly, the requirements will be a systematic approach.
Drug therapy
Medication is the essence of any treatment. Each medication is prescribed by a doctor based on the diagnostic data received. The technique depends on the intensity of the pain syndrome, the stage of progression of the disease.
The following medications are required for back pain:
- NSAIDs(non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) - prescribed in the form of ointments, tablets, injections, sometimes in the form of suppositories. NSAIDs have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects and lower local temperatures.
- painkillersare painkillers that block the nerve centers responsible for recognizing pain.
- Muscle relaxantsare given in cases where muscle cramps need to be eliminated.
- Vitamin complexes,including B vitamins. Their effect contributes to the restoration of nerve fibers and the development of metabolic processes.

The duration of medication, the frequency of medication, and the doses are determined by your doctor.
Massage
A massage course is another effective way to relieve pain. He is appointed when the painful feelings subside and is performed exclusively by a narrow professional.
Massage therapy can stimulate blood circulation, relieve pain, restore nose and muscle flexibility, and more. A massage of at least 10 sessions is required to achieve a tangible effect.
Prevention
To minimize the development of pathologies in which spinal pain is felt or to reduce the risk of disease recurrence, you should follow simple preventive measures:
- Eliminate bad habits.
- Eat eat, eat less fast food, switch to a fractional food system.
- Have an active lifestyle, exercise, preferably swimming, or some form of exercise.
- Useful if your back is hanging on the horizontal bar at least 3-4 times a week.
- Take a break from sitting down to warm up.
- Avoid strenuous physical activity and injury.
- If it is impossible to avoid lifting weights, do everything right, lift heavy things with your back straight.
- Sleep on a medium hard bed, take an orthopedic mattress.
Remember, if the pain lasts longer than 4-5 days, or if the pain is so intense that it is difficult to tolerate, see your doctor immediately. Timely treatment allows you to save your health and avoid many dangerous complications.



































