Exercise is an effective way to treat osteochondrosis: it helps to tone the muscles, improves the functions of the musculoskeletal system and joints. It is recommended to use it in parallel with other methods, such as massage, manual therapy.
Osteochondrosis is a disease of the spine characterized by degenerative lesions of the intervertebral discs that lead to loss of density and integrity (cracks appear). A load on the spine can cause the disc to move toward the spinal canal (a protrusion of the disc) or a protrusion of the nucleus pulposus from the surrounding fibrous ring (intervertebral hernia).
The development of the disease is usually facilitated by a sedentary lifestyle and infrequent physical activity (the tone of the musculoskeletal apparatus of the spine decreases). Special exercises can slow down the course of osteochondrosis.
Regular movement therapy to stretch the vertebrae has a positive effect on the condition of the spine and the body as a whole:
- the back muscles are strengthened;
- improves the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the cartilage and bone tissues of the spine;
- normalizes blood circulation, metabolism in cartilage;
- the process of removing toxins and toxins is accelerated.
Therapeutic practices are used both to alleviate the condition of osteochondrosis and to prevent the development of the disease.
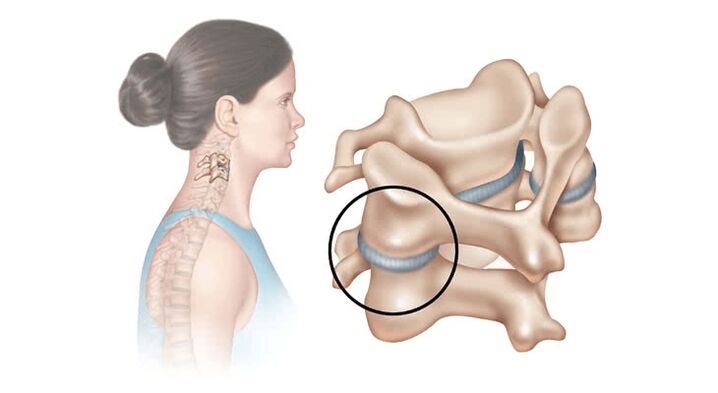
The figure shows a part of the spinal column, the area of the intervertebral disc (between the vertebrae) being circled in black. The intervertebral disc acts as a shock absorber - protecting the vertebrae from friction against each other while walking, sitting and exercising. In addition to an inactive lifestyle, the human body causes metabolic disorders, as a result of which the intervertebral discs do not receive the required amount of nutrients - this is how degenerative changes start, the nucleus pulposus loses moisture, the elasticity of the disc. This in turn leads to an increase in the load on the vertebrae and even the entire spine and back muscles.
The effect of practice
Therapeutic practices are not used during the acute period of osteochondrosis. Stretching along the axis of the spine is prescribed to improve patient well-being. An increase in the distance between the vertebrae leads to muscle relaxation and a decrease in nerve root irritation (pain). As the disease worsens, it is recommended to replace the soft bed with a hard one.
Therapeutic practice has a positive effect in the early stages of osteochondrosis. It stimulates biological and physiological processes within the body: improves blood circulation, improves muscle tone, restores the functions of the spinal movement segment.
In general, regular use of therapeutic exercises will help:
- strengthen the muscles of the hand and the muscle ligament device;
- improves blood flow and lymphatic circulation;
- enhances metabolic processes in the affected tissues of the spine;
- correct incorrect posture;
- restores the supporting and motor functions of the spine.
In the early stages of osteochondrosis, the goal of physiotherapy is to reduce irritation of the nerve roots in contact with the affected intervertebral discs. Despite the positive results of using gymnastics, only exercises that do not cause increased pain should be performed.
Indications for training therapy
The main goal of the exercises is to strengthen the muscle and cartilage tissues that support the vertebrae. The exercises should be done slowly, without sudden movements, completely calmly.
It is not worth overworking during classes: only a moderate load contributes to recovery (improves metabolism, improves the condition of the muscles, restarts the work of the spine, the shock-absorbing functions of the intervertebral discs).
Exercises with acute pain and without prior medical consultation are not recommended. It is better to do physical education under the supervision of a qualified professional (physiotherapist), but you can do it yourself.
To achieve a positive result, you should exercise every day. First, repeat all the exercises up to 5 times, then increase the number of approaches by 10-12 times (as the muscles get stronger).
Frequency of physiotherapy exercises
All exercises prescribed by a doctor for the treatment of osteochondrosis should be performed regularly. In addition, patients whose activities are related to sedentary work are advised to warm up directly at the workplace (preferably, but preferably hourly).
Muscle strengthening is needed every time. Even regular light workouts help prevent a recurrence of the acute phase of osteochondrosis, reducing the intensity of pain.
The effect of physiotherapy practices for spinal diseases can be felt immediately after classes (with appropriately selected gymnastics). The selection of a series of exercises should be done by the physician from the general picture of the disease (stage of development of osteochondrosis, type of damaged structures, form of the disease).
You don't have to stop training. If you feel unwell, there is no relief, consult your doctor: prescribe a new set of exercises.
When is training contraindicated?
Exercises for osteochondrosis improve well-being, preventing the vertebrae from merging during the destructive processes of the spinal plates. Its use is basically recommended for all patients, but exceptions are possible.
Exercise therapy is contraindicated in the following cases:
- the acute period of osteochondrosis;
- postoperative period (in the first stage of spinal restoration);
- neurological diseases accompanied by impaired locomotor coordination;
- hypertension;
- disorders of the vestibular apparatus;
- blurred vision (severe myopia), high intraocular pressure;
- cardiovascular disorders (such as arrhythmia);
- worsening of the patient's condition due to a complication of a chronic illness or serious illness.
Physical education is not done: on an empty stomach, after a meal or physical overtime.
The positive results of the use of physical education are possible with an integrated approach to the implementation of therapeutic practices. In this case, only exercises should be performed that significantly improve the condition of the muscles (increase work capacity, decrease tension).
If you feel worse during or after exercise, it is better to stop and be sure to see a doctor.
Cervical osteochondrosis: what exercises are effective?
The disease manifests itself in different segments of the spine, but degenerative-dystrophic lesions are most commonly observed in the cartilage and bone structure of the cervical region. The main reason is to stay in an uncomfortable, tense situation. People over the age of 25 are most prone to developing the disease.
No special physical training is required to perform physiotherapy exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. All patients can easily perform the following exercises:
- We sit in a chair, straighten our backs, stretch our necks. Then we do 5-10 slow head rotations: left and right (we try to turn the neck as much as possible). The result of physical education is an improvement in the motor functions of the cervical vertebrae.
- In a standing position, tilt your head down, trying to reach your chin to your chest. Repeat the slopes 10 times. (If the chest cannot be reached, we will try to bring our head as close to it as possible).
- We sit down at the table, leaning on our elbows. Place the palm against the temple, tilting the head to the side while creating resistance with your hand (hold in this position for about 10 seconds). The exercise is performed up to 10 times with a break of 8-10 seconds. The effect of performing such an exercise is to strengthen the side muscles of the neck.
- Lie on your stomach to ensure complete relaxation of your muscles. We place our hands along the body (palms up). Then, with slow movements, we turn our head left and then right (up to 10 turns per direction), constantly returning to the starting position: face down.
- We sit down, lean forward, take a deep breath (head touches chest). When we exhale, we return to the starting position, throwing our heads back. The exercise is repeated 10-15 times.
It is recommended to combine each exercise with other types of therapeutic exercises. Systematic performance of such physical education with cervical osteochondrosis strengthens muscles and helps relieve pain.
Exercises for shoulder girdle muscles
The shoulder joint connects the collarbone, the scapula, the armpits, thus providing greater mobility to the upper limb. It leads to a decrease in the functions of the incorrect posture that has developed over the years: the curvature and stiffness of the shoulders appear. With chronic tension in the shoulder girdle, the mobility of the ribs deteriorates and breathing becomes difficult.
Exercises to develop muscles in the shoulder girdle are used to prevent diseases of the spine: osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernia.
It is not recommended to start training without medical advice after injuries or injuries to the shoulder joints.
During the exercise, pay attention to the posture, the correct position of the legs (they should be shoulder-width apart) and the body (you should not lean forward). Only then is the load on the back, arms, neck and shoulder straps evenly distributed.
Do the first exercises slowly and then gradually increase the speed of your movements. This gymnastic technique prevents the onset of muscle pain after a workout.
The shoulder girdle, shoulder development exercises consist of the following exercises:
- We spread our legs shoulder-width apart and put our hands on our belts. We take turns and then turn in the opposite direction.
- I put the injured hand on his healthy shoulder. Place your second hand on the elbow of the unhealthy limb, gently pulling the injured arm up.
- We take our hands behind our backs, locking them so that the patient’s limb is on top. Gently pull the affected arm with the healthy limb down.
This type of exercise improves blood circulation, speeds up metabolic processes in damaged tissues. Gymnastics from the school physical education program has a similar effect.
In osteochondrosis, exertion is undesirable as it may increase pain. Regular light warm-up has a positive effect: cheerfulness appears, the pain goes away.
In case of cervical and shoulder diseases, the use of Dimexide and Bishofit-based compresses is allowed in addition to exercises.
Exercise kit for chest osteochondrosis
Deformity of the spine of the chest region due to poor posture, weakening of the spinal muscles due to lack of regular training. Degenerative changes in this part of the spine often lead to respiratory and cardiovascular disturbances: angina pectoris, arrhythmia, pulmonary and heart failure.
That is why physiotherapy is so important. Performing a properly selected set of exercises will allow you to restart the motor functions of the spinal segments, release blocked vertebrae, and reduce pain attacks.
Removal of the main symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine contributes to physical education, which consists of the following exercises:
- To perform the exercise, take a roller up to 10 centimeters in diameter (a rolled towel will do). We lie on our backs, we put a roller under our chest (lower part). Put your hand under your head, slowly raise your back (repeat several times). Then move the roller along the spine (upwards), repeat the exercise. Uniform examination of different parts of the chest region stretches the spine, tones the muscles.
- Stand on all fours: bend your back as much as possible, stay in this position for a few seconds (keeping your head straight). We then take the starting position and repeat the exercise.
- Lie on your side, bend your knees. Pull the right leg up (stretch the muscles, move the thigh to the side to the maximum), fix the position of the leg for 5-10 seconds, and then lower it. The same is repeated with the second leg.
- We lay down with our bellies on a flat surface, placing our hands under our heads. As we inhale, we lift our shoulders and body, and when we exhale, we return to our starting position. The exercise is performed at least 3-4 times. As the muscles strengthen, we increase the number of approaches.
- We sit on a chair (with our back), leaning on our backs. We lean back to feel the muscles in the chest region stretch. After that, smooth bends are made. 4-5 such approaches should be performed.
Doctors do not recommend muscle overload during exercise therapy. Only moderate gymnastic exercises can bring benefits and pleasure, help to restore the spine after illness.
Exercises for lumbar osteochondrosis
There is an opinion that back pain is mankind’s pay for straight walking. After all, this part of the spine bears the full load while walking and acts as a shock absorber.
Practice shows that people who ignore an active lifestyle are much more likely to suffer from lumbar pain. Daily exercise not only promotes the release of unpleasant pain, but also prevents the development of degenerative-dystrophic processes in the bone and cartilage tissues of the musculoskeletal system.
The therapeutic practice of lumbosacral osteochondrosis strengthens and stretches the back and abdominal muscles. In the first lessons, the exercises are performed lying down: in this situation there is little strain on the back, there is no risk of increased pain.
The positive effects of using the gymnastics are as follows:
- improving blood and lymph circulation;
- normalization of metabolic processes in the bones, cartilage tissues of the spine;
- removing congestion in pelvic organs;
- muscle strengthening;
- pulling the nerve roots of the spinal cord;
- restoration of locomotor system functions.
Gymnastics promotes the production of proteins in muscle tissue. Entering the organization, they stimulate the work of the main systems.
The following exercises can alleviate the condition of lumbar osteochondrosis:
- We lie on our backs, pressing the lower back firmly to the floor, bending our knees. Extend your hands to your feet, trying to hug you (while not tearing your lower back off the floor! ). We stay in this position for 5 seconds, let go, relax the muscles. Repeat the exercise 40 times (for two sets).
- Bring the legs together, pull them to the stomach, bending to the knees. We clasp our legs together with our hands, fix the position, and then slowly extend our heads to our knees. We sink to the floor (slowly), returning to our starting position.
- Stand on all fours, keep your back straight. Cross with your hand to the left, bend your torso in the same direction and then to the right (keep your body bent for several seconds when turning). Repeat the exercise (at least 10 times).
- Starting position - on all fours. Raise your head as you arch your back. Then we do everything in reverse order: we lower our heads, arching our spines smoothly.
- We stand up straight: we keep our feet straight, we put our hands on the belt. If possible, we lean back and forth. You must make 10 deep slopes in each direction.
- We sit on the floor: raising our hands (palms "looking forward"), leaning on our legs, and trying to touch our toes.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis should be aimed at restoring spinal function, relieving pain, and performed in a complex manner. In addition to drug therapy, massage procedures, traction, and physiotherapy practices have a positive effect. Strengthens the muscular corset, helps reduce the load on the spinal plates.



































